If you suspect your uterus size or shape is being affected due to the presence of fibroids, call your doctor right away. Fibroids that result in abdominal swelling or severe symptoms need medical care. At Downtown Vein & Vascular Center, you can look forward to the most advanced and innovative treatments for uterine fibroids. Dr. Sergei A. Sobolevsky uses state-of-the-art diagnostic technology to determine the extent and size of your fibroids and recommends a minimally invasive treatment that works best for you, depending on your fibroid’s size and location.
The uterus is a hollow, upside-down pear-shaped organ in a woman’s pelvis. Also known as the womb, it is the place where a baby grows and develops during pregnancy. It is a thick-walled, muscular organ capable of expansion to accommodate a growing fetus.
A variety of medical conditions can cause the uterus to increase in size, including pregnancy or uterine fibroids. Initial signs of an enlarged uterus include heaviness in the lower abdomen or protruding of the abdomen as the uterus grows in size. There are no other noticeable symptoms.
Read on to understand the causes of an enlarged uterus, how this organ is measured and what makes it average, any health concerns it poses, and how this condition can be treated and managed.
Read more: Why Leg Cramps Happen & When To Worry
How Is a Uterus Measured?
The uterus is measured in three ways:
- Firstly, it is measured by the length, from the fundus, or the part farthest from the opening of the uterus to the outside opening.
- Secondly, it is measured by the width of the uterus, across the fundus.
- Thirdly, it is measured by the thickness of the uterus.
The uterus grows at puberty when it takes a pear shape. At this point, it has reached full size, but the volume will continue to change during a woman’s reproductive years. It changes throughout the menstrual cycle, ranging from 75 ccs to 200 ccs.
What Is the Size of an Average Uterus?
The average size of the uterus is about 3 inches in length, and two inches at the widest part. The uterus can expand up to five times its normal size during pregnancy. It goes from the size of a lemon to the size of a watermelon during the childbearing period.
If your uterus has changed size and you experience other symptoms of uterine fibroids, call your healthcare provider. It is essential to seek medical help before they turn serious and affect your reproductive health or cause further complications.
What are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are abnormal growths that develop in or on the uterus. Also called leiomyomas, they are made up of the muscle and connective tissue from the wall of the uterus. These growths are usually not cancerous, but they can become quite large and cause severe abdominal pain and heavy periods.
Fibroids can grow as a single nodule or growth or in a cluster. The fibroid clusters can range in size from 1 mm to more than 20 cm (8 inches) in diameter or even larger, as large as a watermelon. These growths can develop within the wall of the uterus, inside the main cavity of the organ, or even on the outer surface. Fibroids can vary in size, number, and location within and on the uterus.
Uterine fibroids usually appear in women of childbearing age, generally between 30 to 40 years, but women nearing menopause are at the biggest risk for fibroids.
Read more: What Is A Vein Specialist Called?
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Fibroid symptoms can vary based on size and location in a normal-sized uterus. They may cause very mild symptoms, no symptoms at all, or symptoms that are severe. No two women will experience the same symptoms.
The most common symptoms of uterine fibroids include:
- Heavy, prolonged, or painful periods
- Bleeding between periods
- Pain in the lower abdomen or back
- Severe menstrual cramping
- Stomach swelling
- Anemia
- Bloating
- Constipation
- Painful sex
- Frequent urination
- Discomfort in the rectum
These symptoms can also be similar to other conditions that affect the reproductive system. Thus, it is crucial to seek medical help. The healthcare provider will analyze your symptoms and the level of pain you are experiencing to make an accurate diagnosis and come up with a treatment plan that suits you best.
Read more: Fibroids Bleeding Treatment
How are Uterine Fibroids Diagnosed?
Fibroids are most often found during a physical exam. Your healthcare provider may feel a firm, irregular, usually painless lump during an abdominal or pelvic exam.
Our the best vein doctor may also recommend an ultrasound, MRI, hysterosonography, or hysteroscopy to confirm the diagnosis of uterine fibroids.
Read more: Understanding Uterine Fibroid Size: How Big is Too Big?
Uterus Size and Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are harmless tumors that can grow inside or on the uterus. If the fibroids in the uterus continue to grow, they can change the shape and size of the average uterus. How much the fibroids increase the uterus size will depend on how many fibroids are present, where they are located, and how big they grow.
Fibroids can grow really big and change the average uterus size by causing it to expand. They can start small, about the size of a small seed, and grow quite large, or the size of a grapefruit. Large fibroids are classified as those that range from a grapefruit to a watermelon or are more than 10 cm in diameter. Even medium fibroids can be large enough to increase the size of the uterus. These fibroids may range from the size of a plum to an orange.
If you have multiple fibroids, they can make an average-sized uterus grow and make you look as if you are pregnant. They can expand the uterus to the point that it begins to touch the ribcage. The more the fibroids grow, the more discomfort they can cause. There is also a risk to uterus health and fertility.
How do Fibroids Affect Your Uterus Health?
Fibroids themselves are not usually life-threatening, but they can cause inherent problems. The presence and growth of fibroids can cause the average size of the uterus to change and expand it. They can also cause the uterus to press on other organs, such as the bladder, making it difficult to urinate easily and empty the bladder. You may feel the urge to urinate more often.
Fibroids may also cause heavy bleeding as the pressure makes the endometrial tissue bleed more than usual. They may prevent the uterus from contracting properly to stop menstrual bleeding as expected with a normal period. Larger fibroids can cause more discomfort and embarrassment as they expand your stomach and make it more noticeable.
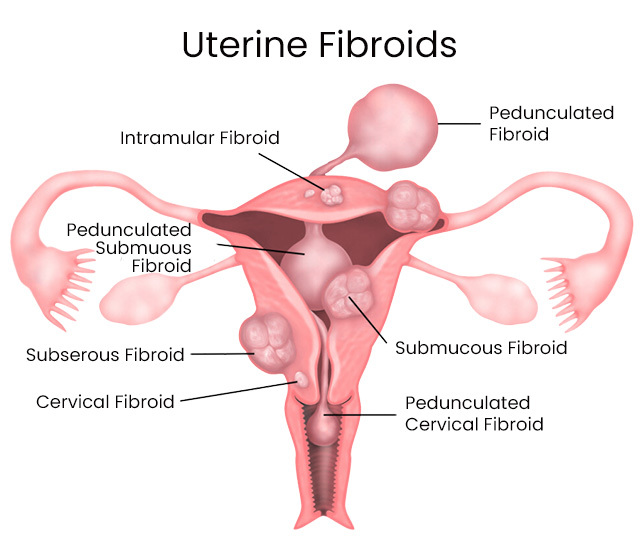
Types of Fibroids
Along with the number and size of fibroids, the type can also affect average uterus size and health.
The three main types of fibroids include:
- Submucosal fibroids – These fibroids are located in the uterus’s inner lining, also known as the endometrium. Submucosal fibroids can grow alone or in a cluster and often cause heavy menstrual bleeding, which can lead to anemia. These fibroids are not very common.
- Subserosal fibroids – These fibroids are found on the outside of the organ, and while they may not change the average uterus size, they can push the uterus into the pelvis. These fibroids can vary in size and location in different areas around the uterus.
- Intramural fibroids – These fibroids develop in the muscular wall of the uterus.
Do Fibroids Affect Pregnant Women?
Yes. Fibroids can cause complications with pregnancy. The size, location, and number of fibroids can affect pregnancy outcomes. They may grow in size during pregnancy due to increased levels of progesterone in the body. They can outgrow their blood supply which may lead to severe pain. Hospitalization may become necessary to monitor the mother and baby’s condition.
Fibroids can also affect the baby’s position in the uterus and increase the risk of miscarriage. They may also increase the risk of preterm delivery and the need for cesarean section delivery. However, many patients with fibroids have safe and healthy pregnancies, as small fibroids do not cause any complications.
Treating Uterine Fibroids
There are many ways to treat fibroids. Your healthcare provider will recommend the best treatment considering your symptoms, age, location of the fibroid, and your plans regarding future pregnancies.
If you only have mild symptoms or no symptoms, your doctor may suggest you wait and see. Fibroids are not cancerous, and they may grow slowly or even shrink after menopause, without affecting your uterus size. Medications for fibroids can ease the symptoms like pain and bleeding and shrink them.
If fibroids continue to grow, the doctor may recommend a minimally invasive treatment to help reduce their size and accompanying symptoms. Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) treats conditions to reduce or eliminate symptoms while keeping the uterus intact. In this procedure, the flow of blood to your fibroids is blocked by inserting gel or plastic particles in the nearby blood vessels. When the fibroid can no longer receive nutrients, it shrinks and dies.
Discover available treatments our fibroid doctors near you in Brooklyn offer:
- Holistic fibroid pain treatment
- Frequent urination treatment
- Fibroid embolization (UFE)
- Fibroid surgery
Our top specialists also provide effective vein treatment options, including:
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors, but they should not be taken lightly, as they can impact your uterus as well as other organs in the body. Visit Downtown Vein & Vascular Center for an accurate diagnosis of your symptoms and their proper treatment to prevent complications to your reproductive health. Dr. Sergei A. Sobolevsky is an endovascular specialist and focuses on delivering the highest level of patient care to ensure your organ health is not affected by these tumors. He also recommends minimally invasive procedures that make treating fibroids both easy and convenient and help your uterus go back to its original size and shape.

Sergei Sobolevsky, MD, is a leading specialist in endovascular medicine with experience in vascular and interventional radiology. Dr. Sobolevsky has decades of experience in the field, with over 25,000 procedures performed, accumulating extensive experience in image-guided minimally invasive medicine, diagnosing and treating a range of conditions.
Dr. Sobolevsky earned his Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree in 1997 from the University of Colorado School of Medicine. He received his specialty clinical training in vascular and interventional radiology at Harvard University. Later, he earned his MBA from the MIT Sloan School of Management. Recognized as a Castle Connolly Top Doctor and named to the Top Doctors New York Metro Area in 2020, 2021, and 2022, Dr. Sobolevsky is licensed in multiple states, has delivered presentations at numerous institutions in the US and abroad, and now acts as a clinical advisor for the biomedical industry. He also held multiple positions in the field during his career, including Chief of Vascular and Interventional Radiology at the Columbia University Medical Center in New York, NY, Senior Vice President in Clinical and Regulatory Affairs at Artann Laboratories in North Brunswick, NJ, and Medical Director at the American Endovascular and Amputation Prevention Center in Brooklyn.
More About Dr. Sobolevsky

